The Importance of Histograms and Descriptive Statistics
Create a Binned Dimension: In the Data pane, right-click (control-click on Mac) a measure and select Create Bins. In the Create Bins dialog box, accept the proposed New field name or specify a different name for the new field. On the web, the dialog box is named Edit Bins and has a slightly different appearance, but the options are the same.
The word “statistics” comes from the German word “stadt”. Stadt means “city” but in the 18th century each city was a state in its own right. And the people who ran those states needed to have the facts. What is the population? What is the food production? How many men are available for the military? What is the birth rate? Information about the state came to be known as Statistics. In today’s complex world people do data mining, gather big data, and perform tests of statistical hypotheses. It is easy to forget that one of the primary tasks of statistics is purely descriptive.
Calculating descriptive statistics such as mean, median, and variance is easy, since Excel has functions for this purpose. Let’s look at something a little more complicated but a necessary tool in the statistician’s toolbox, the frequency distribution and its graphical comrade, the histogram.
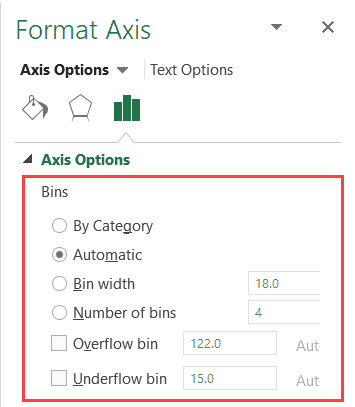
- This is the default setting for histograms. Enter a positive decimal number for the number of data points in each range. Number of bins. Enter the number of bins for the histogram (including the overflow and underflow bins). Overflow bin. Select this check box to create a bin for all values above the value in the box to the right.
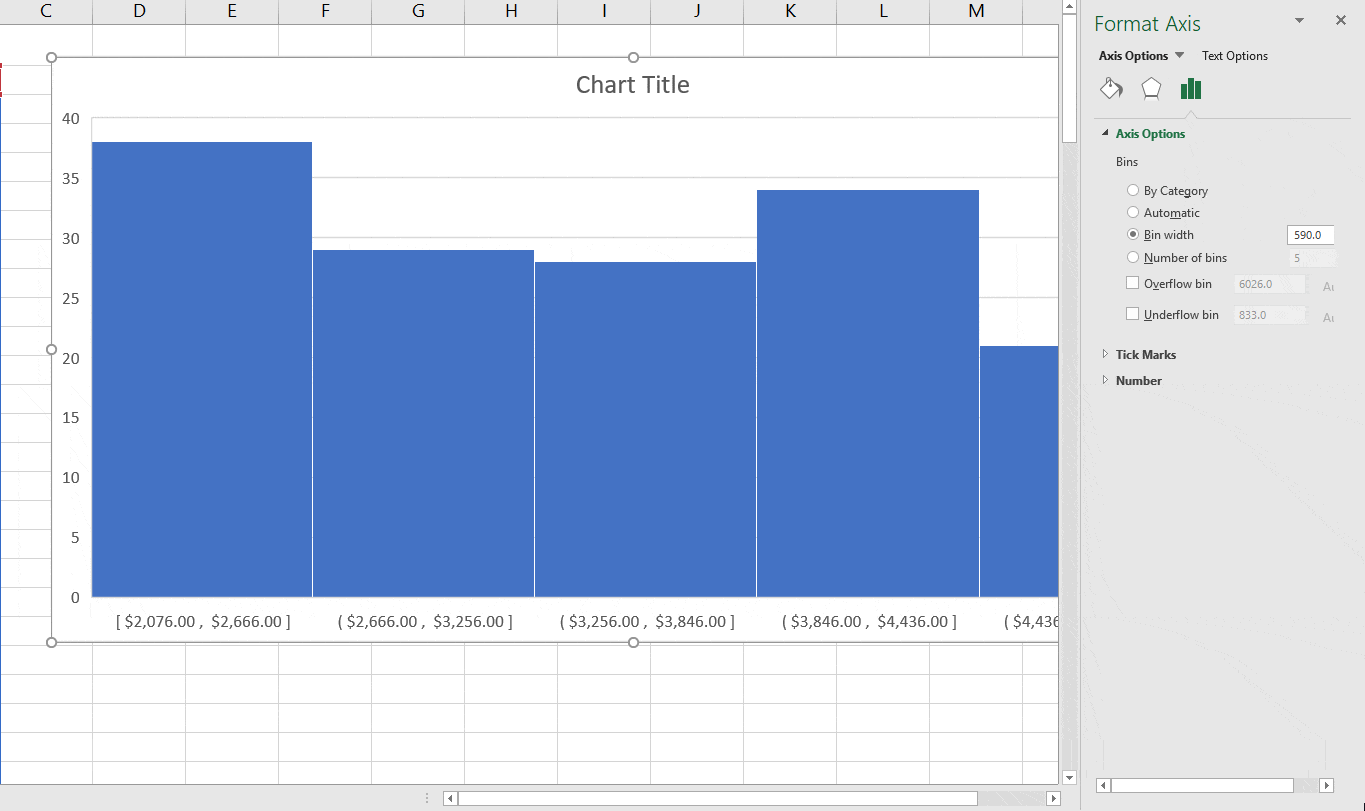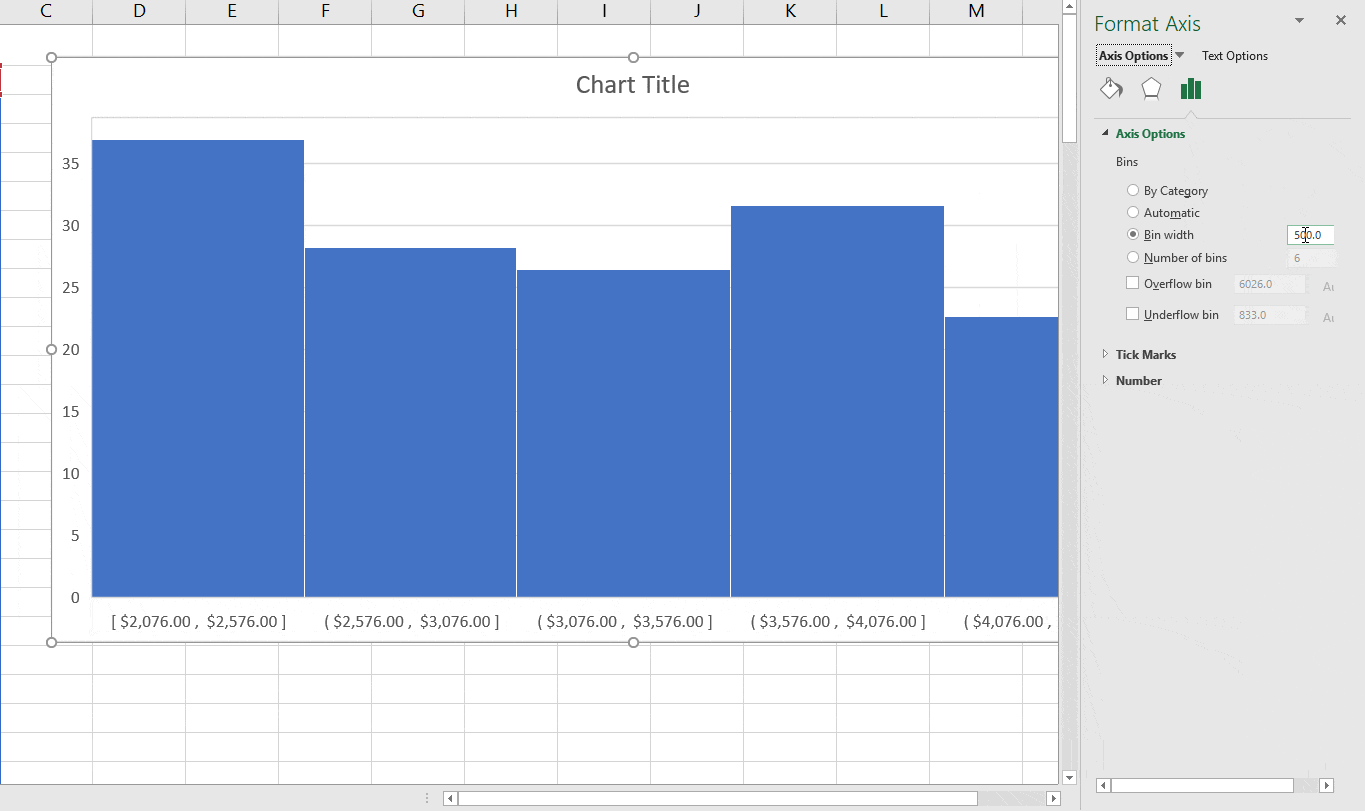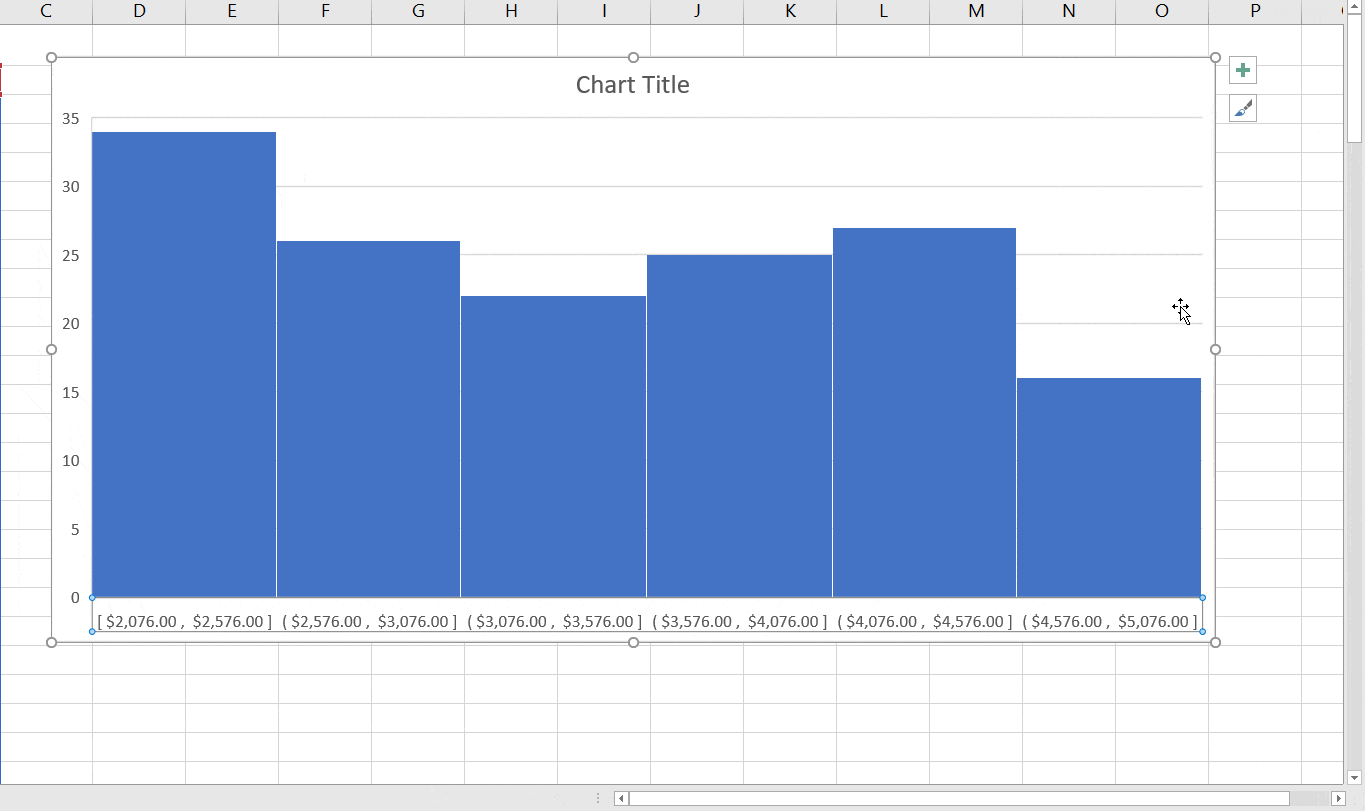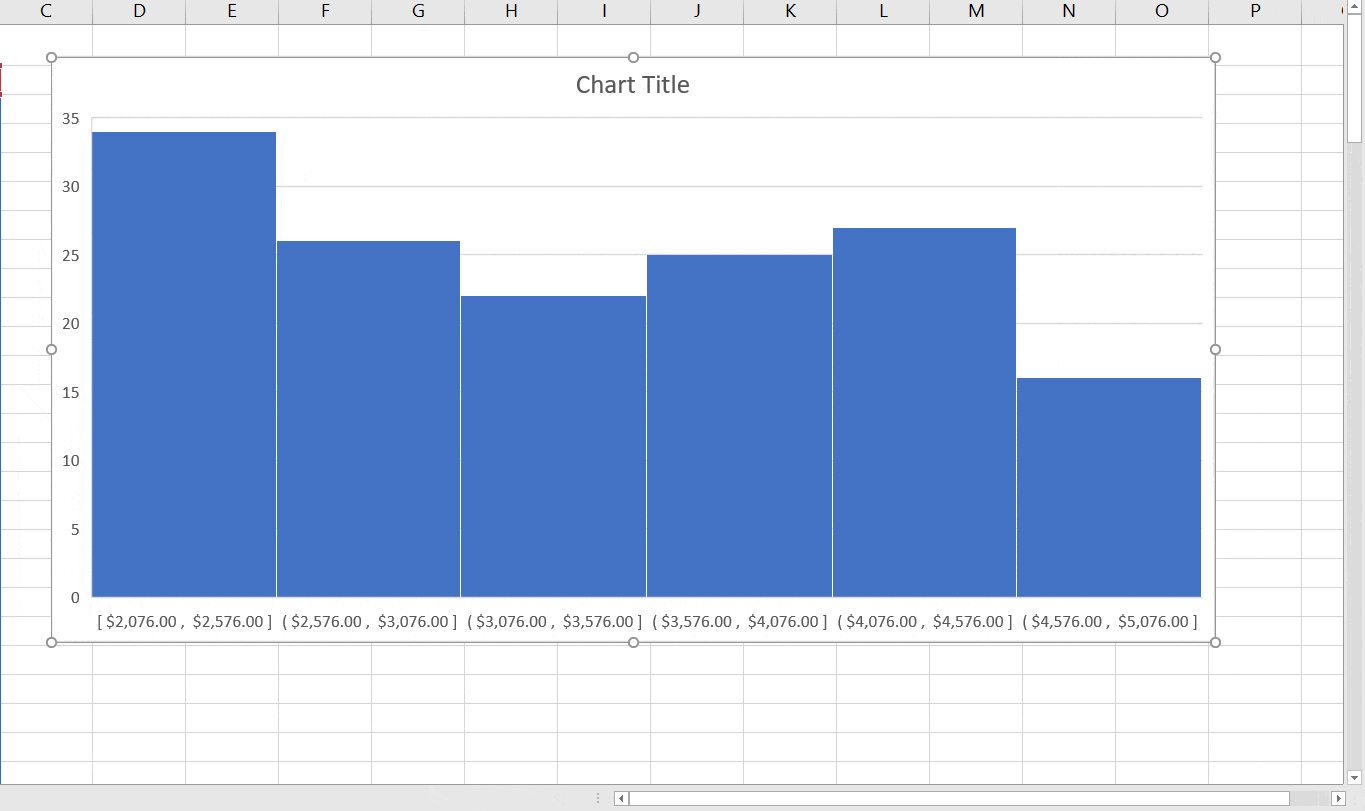
- For example, in our chart, it decided that there should be four bins. You can change this by using the ‘Bin Width/Number of Bins’ options (covered below). Bin Width: Here you can define how big the bin should be. If I enter 20 here, it will create bins such as 36-56, 56-76, 76-96, 96-116.
Creating a Histogram using Microsoft Excel
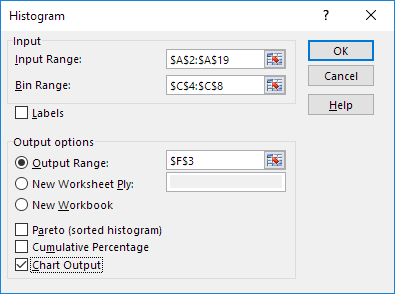
We’ll stick with the centuries-old tradition and gather some information about cities, starting with a table of income information about cities in the United States from the year 2009. We would like to observe the frequency distribution of median family incomes. The Excel data analysis toolpak has a nice dialog box for doing this automatically, but we’re going to take charge and do it ourselves using the FREQUENCY function.
We must first define the bins, which is to say the value ranges into which our data will be sorted. Generally this is done in a worksheet column, and Excel’s auto-fill feature makes this easy. In this example we will create bins from 10,000 to 170,0000 at increments of 5000.

Now we are ready to tabulate our frequency distribution. We highlight a second column next to our column of bin values. In the formula bar, we enter =FREQUENCY(. The first argument is the range containing our data. If you enter this range by highlighting it on the worksheet, be careful not to include the column heading. Only the data is highlighted. The second argument to FREQUENCY is the range containing the bin values. After entering the range in the formula bar close the parenthesis, but
Do not hit enter!
Highlight the range where the frequency results will appear and enter the frequency function.
Enter both the data ranges and the frequency bin range.
You’re almost ready but
Do not hit enter yet!
FREQUENCY if one of the many valuable Excel array functions. Mr. Excel calls them “CSE” functions, and this name is well chosen. The CSE acronym reminds us that you enter array functions not by hitting enter but by hitting <ctrl><shift><enter>. When you hit control-shift-enter, the formua will be entered in the highlighted cells. Note that in the formula bar, the function is now within curly braces. You cannot just type in these curly braces yourself. You must let Excel enter them after you type <ctrl><shift><enter>.
Now that we have our frequency distribution, it is impossible to resist creating a chart. The frequency range is already highlighted; we have only to click on “column chart” from Excel’s Insert ribbon tab. The chart looks OK, but we see that we will have to edit the horizontal axis label to reflect our frequency bins. We can right-click on the chart and choose “Select Data…” . Click the “Edit” button on the right-hand side, the side for the horizontal axis labels. Then enter the range containing the frequency bins.
Right-click the chart and choose “Select Data…” to edit the axis labels.
Right-click the chart and choose “Select Data…” to edit the axis labels.
After entering a title and choosing a style, we have our finished frequency histogram!
I hope you enjoyed my first Excel post! Stay tuned for my next one where we cover Standard Deviations.
A histogram uses bars to visualize the distribution of data for how many things, people, or occurrences happened between a range of values on an axis. While histograms look like bar charts, they are different in that each bar is an interval of values of a metric. These bars are called bins or buckets, and together they represent what is called a frequency distribution. A frequency distribution is the display of how often something occurred in a graph, table, or diagram. Histograms are graphs and are one way to visualize frequency distributions.
You’ve probably seen a histogram searching for the best time to visit a restaurant on Google!
This histogram shows the frequency of visitors to a restaurant in one hour bins within the range of a time frame. However, not all histograms need to use a time period as the given range.
Histograms in statistics
Histograms are useful for analyzing numerical data sets. Analysts and statisticians use them to analyze patterns of frequency, and visualize a numerical breakdown of what is being collected in the data.
In statistics, histograms are used to graph the probability distribution of the data. This represents the percentage rate chance of any particular data point falling within each range. A probability histogram showcases the data point values that are most likely to occur. A common example is a dice roll, by calculating and displaying the predicted frequency distribution of the different numbers that the dice may land on.
A quick breakdown of histogram data
The bars in a histogram represent numeric bins (Ex. 0-19, 20 - 39, 40- 59, etc.) with data bucketed into a given range (Ex. 0 -100). The distribution that is displayed in the visualization is based on how the bins are divided. For example, you could divide the range 0 - 100 by 5 bins or by 4 bins, making the bin interval either 20 or 25 units.
This guide explains how to make a histogram in Tableau (version 2020.2), Excel 2016 + (version 16.XX), or Google Sheets. Consider using Tableau Desktop for free.
Download the example Excel data to follow along in any tool.
To make a histogram, follow these steps.
How To Modify Bin Width In Excel On Mac
